RMM software features essential for proactive network monitoring and alerts are a game-changer for IT. Imagine a world where network outages are predicted and prevented, not just reacted to. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the reality RMM offers. By leveraging real-time monitoring, automated alerts, and remote access capabilities, businesses can significantly reduce downtime and enhance overall network stability.
This deep dive explores the key features that make this possible, transforming reactive IT into a proactive powerhouse.
We’ll explore the core monitoring functionalities, delve into sophisticated alerting systems, examine the power of remote access and control, and uncover the insights provided by robust reporting and analytics. We’ll also look at how seamless integration with other IT tools enhances efficiency and streamlines workflows, giving you a complete picture of how RMM software contributes to a more resilient and responsive IT infrastructure.
Get ready to level up your network management game!
Essential Monitoring Capabilities: RMM Software Features Essential For Proactive Network Monitoring And Alerts
Proactive network monitoring is crucial for maintaining a healthy and efficient IT infrastructure. RMM (Remote Monitoring and Management) software plays a vital role in this process, providing the tools and insights necessary to identify and address potential issues before they escalate into major outages. By automating monitoring and alerting, RMM solutions significantly reduce downtime and improve overall network performance.Real-time performance monitoring is the cornerstone of proactive network management.
This capability allows IT administrators to observe key network metrics in real-time, providing an immediate understanding of the network’s health and performance. This constant visibility enables quick identification of emerging problems, such as slow response times, high CPU utilization, or memory leaks, before they impact end-users or critical applications.
Automated Alerts Based on Predefined Thresholds
RMM software empowers administrators to set up automated alerts based on predefined thresholds for various network parameters. This means that when a specific metric, like CPU usage, crosses a predetermined limit (e.g., 90%), the system automatically generates an alert, notifying the IT team of the potential problem. These alerts can be delivered through various channels, including email, SMS, or in-app notifications, ensuring timely response and resolution.
The ability to customize these thresholds based on specific network needs ensures that alerts are relevant and prevent alert fatigue.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) Tracked by Effective RMM Solutions
Effective RMM solutions track a wide range of KPIs to provide a comprehensive overview of network health. These KPIs offer insights into various aspects of network performance, enabling proactive identification and resolution of potential issues. Examples include: CPU utilization, memory usage, disk space, network bandwidth, response times, and application performance. Tracking these metrics allows IT teams to pinpoint bottlenecks and optimize resource allocation for improved performance and stability.
For instance, consistently high CPU utilization might indicate the need for hardware upgrades or software optimization, while low disk space could signal the need for data cleanup or storage expansion.
Comparison of RMM Software Approaches to Network Monitoring
The following table compares different RMM software approaches to network monitoring, highlighting their key features, alerting mechanisms, and pricing models. Note that pricing can vary significantly based on the number of devices managed, features included, and support level.
Proactive network monitoring using RMM software is crucial for preventing IT disasters. Choosing the right features is just as important as, say, comparing different HRIS vendors and selecting the best fit for your business needs. Both processes require careful consideration of functionalities and long-term implications to ensure optimal performance and minimize disruptions. Ultimately, effective RMM software, like a well-chosen HRIS, contributes to a smoother, more efficient operation.
| Software Name | Key Features | Alerting Mechanisms | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atera | Real-time monitoring, automated alerts, remote control, patch management | Email, SMS, in-app notifications | Subscription-based, tiered pricing |
| Datto RMM | Comprehensive monitoring, automated scripting, remote access, security features | Email, SMS, webhooks | Subscription-based, tiered pricing |
| ConnectWise Automate | Extensive monitoring capabilities, automation tools, remote control, reporting | Email, SMS, custom integrations | Subscription-based, tiered pricing |
| NinjaOne | Unified platform for RMM and PSA, automated patching, security features | Email, SMS, in-app notifications, custom integrations | Subscription-based, tiered pricing |
Alerting and Notification Systems
Proactive network monitoring is only half the battle; effective alerting ensures you’re notified immediately when issues arise, allowing for swift resolution and minimized downtime. A robust alerting system is the backbone of any successful RMM strategy, transforming passive monitoring into active problem-solving. The right system will dramatically improve your response time and overall IT efficiency.Alert delivery methods significantly impact response time and the effectiveness of your IT team.
Choosing the right method depends on factors such as urgency, recipient availability, and preference. A multi-faceted approach is often the most effective strategy.
Alert Delivery Methods
RMM software offers a variety of methods to deliver alerts, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Email remains a popular choice for less critical alerts or summaries, offering a detailed record of past issues. SMS messages, on the other hand, are ideal for urgent situations requiring immediate attention, ensuring the notification is seen quickly, even if the recipient isn’t at their computer.
Push notifications, delivered directly to mobile devices, offer similar immediacy to SMS, often integrating with existing communication apps for seamless integration into workflows. Choosing the right method often involves prioritizing urgency and recipient preferences. For example, a minor storage threshold breach might warrant an email, while a server crash demands immediate SMS or push notification alerts.
Customizable Alert Thresholds and Escalation Rules
The ability to customize alert thresholds is crucial for preventing alert fatigue and ensuring only genuinely critical issues trigger notifications. Setting thresholds too low leads to a flood of irrelevant alerts, while setting them too high risks missing important problems. For example, a CPU utilization threshold of 90% might trigger an alert, while 80% might only generate a warning.
Similarly, escalation rules define how alerts are handled if not addressed within a specified timeframe. This might involve escalating the alert to a senior technician or triggering automated responses, such as restarting a service. This layered approach ensures that even if an initial alert is missed, the issue doesn’t go unnoticed.
Integration with ITSM Systems
Integrating RMM alerts with existing ITSM (IT Service Management) systems, such as ServiceNow or Jira, streamlines incident management. This integration automatically creates tickets upon alert generation, providing a centralized platform for tracking and resolving issues. It also ensures consistent logging and reporting, providing valuable data for identifying recurring problems and improving overall IT performance. This integration eliminates the need for manual ticket creation, reducing workload and improving response times.
Best Practices for Alert Management
Effective alert management requires a proactive approach. Regularly review and adjust alert thresholds and escalation rules based on historical data and changing system requirements. Implement a robust system for acknowledging and responding to alerts, assigning responsibility and tracking resolution times. Regular training for IT staff on alert procedures is essential, ensuring everyone understands their roles and responsibilities in responding to different alert types.
Proactive network monitoring, a key feature of robust RMM software, ensures smooth operations by sending timely alerts. This preventative approach mirrors the importance of best practices for HRIS data management and reporting , where proactive data handling prevents future HR headaches. Similarly, effective RMM software helps you stay ahead of potential IT issues, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
Finally, regularly analyze alert data to identify trends and patterns that might indicate underlying system issues, allowing for preventative maintenance.
Alert Workflow Diagram
Imagine a flowchart: The process begins with a monitored system (e.g., a server) exceeding a predefined threshold (e.g., high CPU usage). This triggers an alert within the RMM software. The alert is then sent via chosen channels (email, SMS, push notification) to designated personnel. The recipient acknowledges the alert and begins troubleshooting. Once the issue is resolved, the alert is closed within the RMM system and the ITSM system (if integrated).
This entire process is logged for future analysis and reporting. The diagram visually represents this sequence, clearly outlining each step and the associated responsibilities.
Remote Access and Control Features
Remote access capabilities within RMM software are game-changers for proactive network management. They allow IT professionals to address issues swiftly and efficiently, minimizing downtime and preventing potential escalations. This proactive approach is far more effective than simply reacting to reported problems.Remote access facilitates proactive problem-solving by enabling IT teams to directly investigate and resolve issues on end-user devices or servers without physical presence.
This speed drastically reduces resolution times, improves user experience, and prevents minor problems from developing into major outages. For example, a slow-performing application can be diagnosed and optimized remotely, preventing user frustration and potential productivity losses.
Security Implications of Remote Access and Best Practices for Secure Connections
The inherent convenience of remote access also introduces security risks. Unauthorized access can lead to data breaches, malware infections, and significant financial losses. Implementing robust security measures is paramount. Secure connections should always leverage encryption protocols like SSH or HTTPS, ensuring all data transmitted between the RMM software and the remote device is unreadable to unauthorized parties. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of protection, requiring multiple verification steps before granting access.
Regular security audits and updates to the RMM software and all connected systems are also crucial.
Comparison of Remote Control Methods Offered by RMM Software
Various remote control methods exist within RMM software, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some offer full control, mirroring the remote device’s screen and allowing for complete management. Others provide a more limited, task-specific approach, perhaps only allowing file transfers or the execution of pre-defined scripts. The choice depends on the specific needs of the organization and the level of access deemed necessary.
For example, a help desk agent might only need limited access to troubleshoot a specific application, while a system administrator requires full control for more complex tasks. A robust RMM platform will likely offer a range of options, allowing administrators to tailor access levels to specific situations and users.
Examples of Scenarios Where Remote Access Prevents Network Issues
Consider a scenario where a critical server experiences a sudden performance drop. With remote access, an administrator can immediately log in, diagnose the problem (perhaps a resource bottleneck or a failing component), and take corrective action, preventing widespread service disruption. Similarly, a user reporting a persistent application error can have the issue resolved remotely, eliminating the need for an on-site visit and minimizing downtime.
Remote patching and software updates are also facilitated, proactively addressing vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by malicious actors.
Security Measures to Implement When Using Remote Access Features in RMM Software, RMM software features essential for proactive network monitoring and alerts
Implementing robust security is vital. A comprehensive approach includes:
- Strong Passwords and MFA: Enforce strong, unique passwords for all user accounts and implement multi-factor authentication for enhanced security.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs): Use ACLs to restrict access to sensitive systems and data based on the principle of least privilege.
- Encryption: Ensure all remote access connections are encrypted using robust protocols such as SSH or HTTPS.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep the RMM software, operating systems, and applications on all managed devices up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): Implement IDS/IPS to monitor network traffic and detect suspicious activity.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Use SIEM to centralize security logs and monitor for threats.
Reporting and Analytics
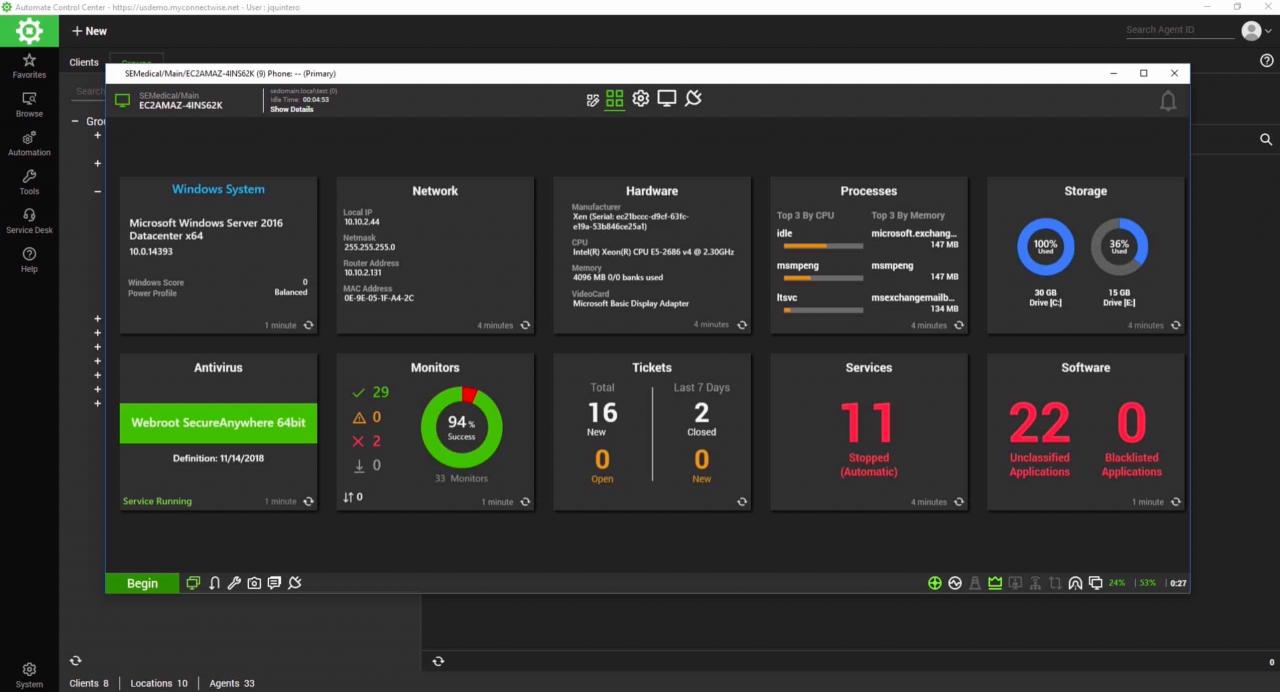
Proactive network management isn’t just about reacting to problems; it’s about anticipating them. Comprehensive reporting and analytics are the key to unlocking this predictive power, transforming your RMM software from a reactive tool into a strategic asset. By analyzing historical data and identifying emerging trends, you can significantly reduce downtime and optimize network performance.Reporting provides a clear, concise overview of your network’s health and performance, allowing you to quickly identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
This data-driven approach empowers informed decision-making, leading to more efficient resource allocation and improved overall network stability. Essentially, robust reporting transforms raw data into actionable insights.
Network Health Reports
These reports provide a holistic view of your network’s current status. They typically include metrics like device uptime, bandwidth usage, and error rates. By visualizing this information through charts and graphs, you can easily spot anomalies and potential issues. For example, a sudden spike in error rates on a specific server could indicate an impending hardware failure, allowing for proactive intervention and preventing a service outage.
Visualizations like line graphs effectively show trends over time, while pie charts illustrate the proportion of resources consumed by different applications or devices.
Trend Analysis and Predictive Capabilities
Analyzing historical data through reporting reveals patterns and trends that can predict future network behavior. For example, consistently increasing bandwidth usage during specific times of day might indicate a need for capacity upgrades. Similarly, a gradual increase in latency over several weeks could signal a developing network congestion issue. By identifying these trends early, you can proactively implement solutions, such as upgrading hardware or optimizing network configurations, to prevent future problems.
This predictive capability is crucial for maintaining optimal network performance and minimizing disruptions.
Example Report: Key Network Metrics
The following table showcases a sample report displaying key network metrics, providing a snapshot of the network’s health. The “Trend” column indicates whether the metric is improving, worsening, or stable. This type of report is easily generated by most RMM software with reporting capabilities.
| Metric | Value | Status | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPU Utilization (Server A) | 75% | Warning | Increasing |
| Network Latency (Branch Office) | 20ms | Normal | Stable |
| Disk Space (Server B) | 90% | Critical | Increasing |
| Bandwidth Usage (Total) | 850 Mbps | Normal | Stable |
Data Visualization Techniques
Effective data visualization is crucial for understanding complex network data. Different chart types are suited for different types of data and insights. Line graphs are excellent for showing trends over time, such as bandwidth usage or latency. Bar charts are useful for comparing different metrics across various devices or locations. Pie charts effectively illustrate the proportion of resources consumed by different applications or services.
Heatmaps can visually represent the density of network traffic across different time periods or geographic locations. By utilizing a variety of visualization techniques, you can effectively communicate complex network information to both technical and non-technical audiences.
Integration with Other Tools

RMM software’s power significantly expands when integrated with other IT tools. This interconnectedness creates a more efficient and streamlined IT management ecosystem, moving beyond isolated functionalities to a holistic approach. Effective integration allows for automated workflows, reduced manual tasks, and improved overall visibility across your IT infrastructure.Seamless integration streamlines workflows and boosts efficiency by eliminating data silos and automating repetitive tasks.
Imagine a scenario where a network alert triggers an automatic ticket creation in your help desk system, simultaneously notifying the relevant technician. This eliminates manual data entry, reducing human error and significantly speeding up response times. The benefits extend to improved collaboration between teams and a more proactive approach to problem-solving.
Benefits of RMM Integration with Ticketing and PSA Systems
Integrating your RMM software with ticketing systems (like Zendesk, Jira Service Desk) and Professional Services Automation (PSA) software (like Autotask PSA, ConnectWise Manage) offers substantial advantages. Ticketing system integration allows for automated ticket creation based on RMM alerts, providing a centralized location for managing and tracking incidents. PSA integration enhances this further by linking tickets to projects, resources, and billing information, providing complete visibility into the lifecycle of IT issues.
This integrated approach offers better resource allocation, improved customer communication, and enhanced reporting capabilities.
Challenges in Integrating RMM Software with Other Systems
While the benefits are clear, integrating RMM with other systems can present challenges. Data format discrepancies between different systems often require custom scripting or API workarounds. Security concerns related to data sharing between different platforms need careful consideration and robust security protocols. Finally, ensuring consistent data synchronization and preventing conflicts across integrated systems demands thorough planning and testing.
Choosing compatible systems with well-documented APIs can mitigate many of these challenges.
Examples of Successful RMM Integrations and Their Benefits
A successful integration example involves using an RMM solution to monitor server health, automatically generating tickets in a help desk system when critical thresholds are breached. The technician receives an alert, accesses the server remotely via the RMM, and resolves the issue. The entire process is documented within the ticketing system, improving accountability and allowing for better performance analysis.
Another example is the integration of RMM with a PSA system, allowing for accurate time tracking on service tickets directly related to RMM-detected issues, leading to more precise billing and project management. This integrated approach streamlines operations and provides valuable insights into IT costs and efficiency.
Enhanced Proactive Monitoring through Integrated Tool Data
Data from integrated tools significantly enhances proactive monitoring capabilities. By correlating data from your RMM, ticketing system, and network monitoring tools, you gain a comprehensive understanding of your IT environment. For instance, combining RMM performance data with user support tickets can reveal patterns indicating underlying infrastructure problems, allowing for proactive remediation before impacting users. This holistic view moves beyond reactive problem-solving to a proactive approach focused on preventing issues before they arise.