Best practices for HRIS data management and reporting are crucial for any organization aiming for efficient HR operations and strategic decision-making. This isn’t just about storing employee data; it’s about leveraging that data to improve everything from recruitment and onboarding to performance management and compensation. We’ll explore key strategies for ensuring data security, accuracy, and accessibility, ultimately transforming HR data into a powerful tool for growth and success.
From navigating complex data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA to mastering data integration and building robust reporting systems, this guide offers a comprehensive look at optimizing your HRIS data. We’ll uncover the secrets to effective data governance, explore methods for preventing data errors, and delve into the art of creating insightful HR reports that truly inform strategic initiatives.
Get ready to unlock the full potential of your HRIS data!
Data Security and Compliance: Best Practices For HRIS Data Management And Reporting
Protecting HRIS data is paramount, not just for maintaining employee trust but also for adhering to increasingly stringent legal requirements. A breach can lead to significant financial penalties, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Robust security measures are therefore crucial for any organization handling sensitive employee information.
Data encryption and access controls are foundational elements of a secure HRIS system. Encryption safeguards data both in transit and at rest, making it unreadable to unauthorized individuals even if intercepted. Access controls, on the other hand, limit who can view, modify, or delete specific data based on their roles and responsibilities within the organization. This principle of least privilege ensures that only authorized personnel have access to necessary information, minimizing the risk of data breaches caused by insider threats or accidental exposure.
Mastering best practices for HRIS data management and reporting is key to efficient HR operations. A crucial aspect of this involves ensuring accurate and timely data flow, which is significantly enhanced by integrating HRIS with payroll and benefits administration systems seamlessly. This integration streamlines processes and minimizes errors, ultimately improving the overall quality of your HRIS data and reporting capabilities.
Data Privacy Regulation Compliance, Best practices for HRIS data management and reporting
Compliance with regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) is non-negotiable for organizations handling personal employee data. These regulations mandate specific measures to protect personal information, including data minimization, purpose limitation, and the right to access, rectification, and erasure of data. Organizations must implement processes for handling data subject requests, ensuring transparency about data collection and usage, and implementing appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect against unauthorized access or processing.
Failure to comply can result in hefty fines and severe reputational damage. For example, a company failing to properly secure employee data under GDPR could face fines up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher.
Authentication and Authorization Methods
Strong authentication methods are essential for verifying the identity of users attempting to access the HRIS system. Multi-factor authentication (MFA), which requires users to provide multiple forms of verification (e.g., password, one-time code from a mobile app, biometric scan), significantly enhances security compared to password-only authentication. Authorization mechanisms then determine what actions a user is permitted to perform once authenticated.
Role-based access control (RBAC) is a common approach, assigning users to specific roles with predefined permissions. For instance, a payroll administrator might have access to salary information but not performance reviews, while a hiring manager might have access to candidate data but not employee compensation details.
Data Security Measures and Effectiveness
| Security Measure | Description | Effectiveness | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Encryption | Transforms data into an unreadable format | High | Encrypting sensitive data like salary information both in transit (using HTTPS) and at rest (using database encryption). |
| Access Controls | Limits user access based on roles and permissions | High | Using RBAC to restrict access to payroll data to only authorized personnel. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Requires multiple verification methods for login | Very High | Requiring a password and a one-time code from a mobile authenticator app for access. |
| Regular Security Audits | Periodic assessments of security posture | Medium to High (depending on frequency and thoroughness) | Conducting annual penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities. |
Data Integration and Interoperability
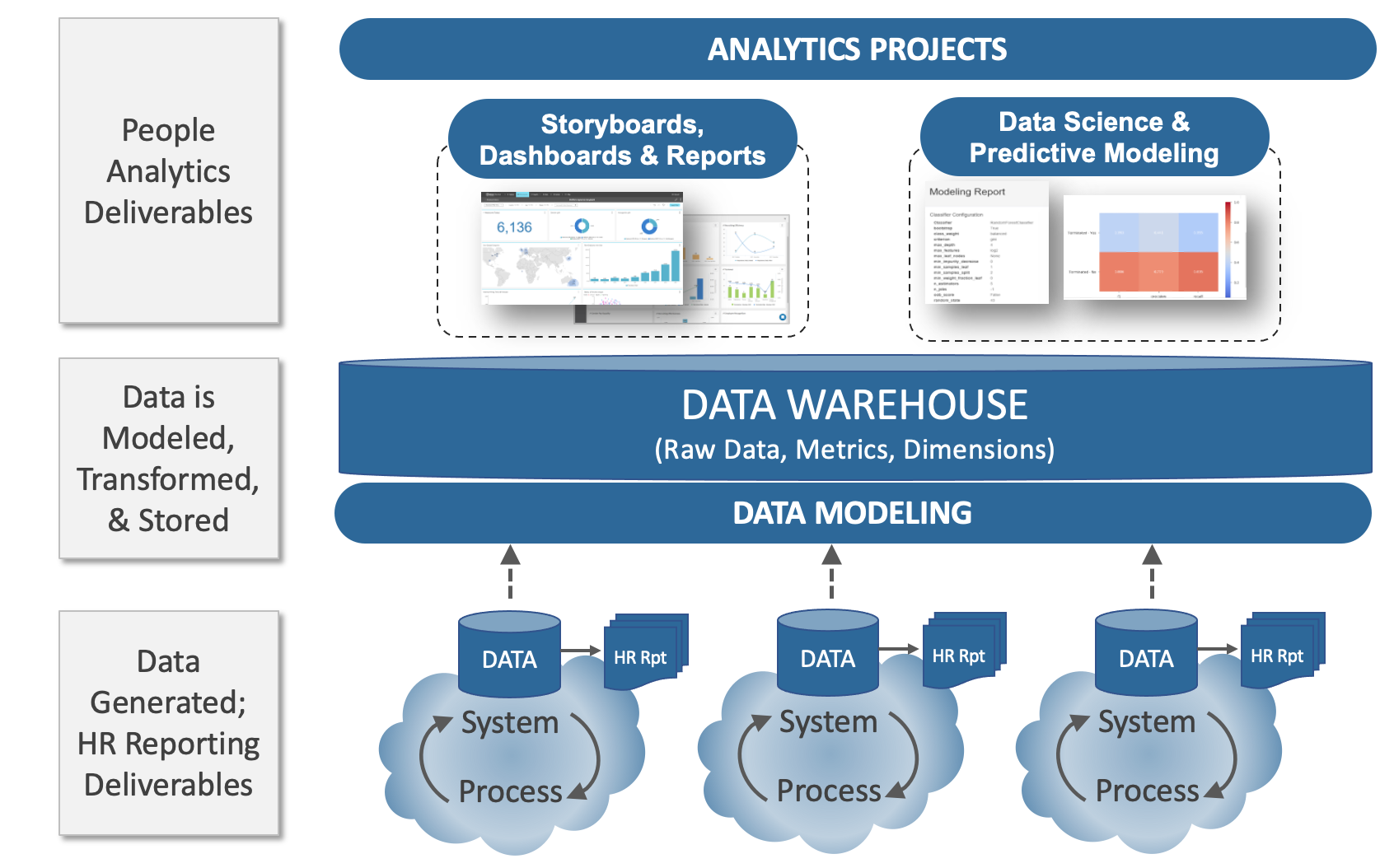
Integrating your HRIS with other enterprise systems is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity for modern HR. Seamless data flow unlocks powerful insights, streamlines processes, and ultimately boosts efficiency and strategic decision-making. This section dives into the best practices for achieving this crucial integration, ensuring data accuracy, and handling any discrepancies that might arise.
The benefits of a well-integrated HRIS are numerous. Imagine having a single source of truth for all employee data, effortlessly accessible across departments. This eliminates data silos, reduces manual data entry, and minimizes the risk of errors. For example, integrating your HRIS with your payroll system ensures that salary information is automatically updated, preventing discrepancies and delays in payments.
Similarly, integrating with your performance management system provides a holistic view of employee performance, enabling more informed decisions about promotions, training, and compensation.
Best Practices for Data Consistency and Accuracy
Maintaining data consistency and accuracy across integrated systems requires a proactive and structured approach. This involves establishing clear data governance policies, defining data standards, and implementing robust data validation rules. Regular data quality checks and reconciliation processes are also crucial. For instance, implementing automated data cleansing routines can identify and correct inconsistencies in employee data before they propagate throughout the system.
Furthermore, establishing a centralized data dictionary defining all data fields and their meanings ensures everyone uses the same terminology and data formats.
Best practices for HRIS data management and reporting hinge on accurate, readily available information. To truly leverage your data, however, you need a system that supports more than just record-keeping; check out these top HRIS features for improving employee engagement and productivity to understand how insightful data drives better decision-making. Ultimately, effective HRIS reporting relies on a robust system that provides actionable intelligence, leading to more strategic HR initiatives.
Methods for Handling Data Discrepancies
Despite best efforts, discrepancies between integrated systems can occur. A robust process for identifying, investigating, and resolving these discrepancies is vital. This often involves establishing clear escalation paths and assigning responsibility for data reconciliation. Automated alerts can flag potential inconsistencies, allowing for prompt intervention. For example, if an employee’s address differs between the HRIS and the payroll system, an alert can be triggered, prompting an investigation to determine the correct information and update both systems accordingly.
Reconciliation reports should be generated regularly to track and monitor the resolution of discrepancies.
Data Integration Process Flowchart
Imagine a flowchart depicting the data integration process. It would begin with the identification of data sources (HRIS, payroll, performance management, etc.). Next, data extraction would occur from these sources, followed by data transformation to ensure consistency in format and structure. Then, data validation would take place to check for accuracy and completeness. After validation, data loading into the target system (often a data warehouse or a central repository) would occur.
Finally, data monitoring and reconciliation would ensure the continued accuracy and consistency of the integrated data. The entire process would ideally be automated to minimize manual intervention and maximize efficiency.
Data Quality and Validation
Maintaining high-quality data within your HRIS is crucial for accurate reporting, effective decision-making, and compliance. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to flawed analyses, inefficient processes, and even legal issues. This section explores common data errors, validation methods, data cleansing techniques, and best practices for preventing future issues.Data quality issues can significantly impact the reliability of HR metrics and analytics.
Poor data quality can lead to inaccurate compensation calculations, flawed performance reviews, and inefficient talent management strategies. Addressing data quality proactively is essential for optimizing HR operations and making informed decisions.
Common Sources of Data Errors in HRIS Systems
Several factors contribute to data errors within HRIS systems. These include manual data entry mistakes (typos, incorrect formatting), inconsistencies in data entry practices across different departments, outdated or incomplete employee information, system glitches or bugs, and the integration of data from disparate sources that may use conflicting formats or definitions. For example, inconsistencies in date formats or the use of different abbreviations for job titles can lead to significant data discrepancies.
Similarly, data migration from legacy systems can introduce errors if not properly handled. Another example is the manual updating of employee contact information, which may lead to outdated or incorrect data if not regularly checked and verified.
Methods for Validating Data Accuracy and Completeness
Validating data accuracy involves employing various techniques to ensure the data reflects reality. This can involve automated checks such as data type validation (ensuring numbers are in the correct format, dates are valid, etc.), range checks (verifying values fall within acceptable limits), and cross-field validation (checking for consistency between related data fields). Manual validation may also be required, such as reviewing a sample of employee records for accuracy or comparing HRIS data to other reliable sources.
Regular data audits, scheduled at intervals appropriate to the organization’s size and complexity, are also crucial for detecting and correcting errors.
Data Cleansing Techniques
Data cleansing, also known as data scrubbing, involves identifying and correcting or removing inaccurate, incomplete, irrelevant, duplicated, or improperly formatted data. Techniques include standardization (e.g., converting date formats to a consistent standard), deduplication (removing duplicate records), and parsing (extracting specific information from unstructured data fields). For instance, standardizing job titles by using a controlled vocabulary ensures consistency across the system.
Deduplication helps remove duplicate employee records, often arising from data entry errors or merging data from different sources. Parsing can be used to extract relevant information from free-text fields, such as employee comments in performance reviews, to categorize data effectively.
Best Practices for Preventing Data Errors During Data Entry and Updates
Preventing data errors requires a proactive approach. This includes implementing data entry validation rules to prevent incorrect data from being entered, providing comprehensive training to HR staff on data entry procedures, using data entry tools with features such as auto-completion and drop-down menus to reduce manual typing errors, and establishing clear data governance policies that define data standards and responsibilities.
Regular data backups are essential to ensure data recovery in case of accidental deletion or system failures. Implementing a workflow process for data updates, with appropriate approvals and checks, can minimize the risk of errors. Furthermore, encouraging employee self-service for updating their own information, with appropriate validation rules in place, can improve data accuracy and reduce the burden on HR staff.
Data Governance and Management
Effective HRIS data governance is the cornerstone of a robust and reliable HR system. It ensures data accuracy, consistency, and accessibility, ultimately supporting better decision-making and strategic HR planning. Without a strong governance framework, data quality suffers, leading to inaccurate reporting, inefficient processes, and potential compliance issues.
Data governance encompasses the policies, processes, and technologies used to manage the entire lifecycle of HR data. This includes defining roles and responsibilities, establishing data quality standards, and implementing controls to ensure data integrity and security. A well-defined governance framework provides a clear roadmap for managing HR data, minimizing risks, and maximizing the value of HRIS investments.
Roles and Responsibilities of Key Stakeholders in HRIS Data Governance
Establishing clear roles and responsibilities is crucial for successful HRIS data governance. Each stakeholder plays a vital part in ensuring data quality and compliance.
- Data Owner: Typically a senior HR leader, responsible for the overall quality, integrity, and compliance of HR data. They define data policies and ensure their implementation.
- Data Steward: Responsible for the day-to-day management of specific datasets within the HRIS. They ensure data accuracy, completeness, and consistency.
- Data Custodian: Responsible for the technical aspects of data management, including storage, security, and access control. This role is often filled by IT professionals.
- HR Business Partners: Act as liaisons between HR and business units, ensuring data needs are met and data is used effectively for decision-making.
- Employees: Responsible for providing accurate and up-to-date information when requested. Data governance training is key for employee understanding and compliance.
Establishing and Maintaining Data Governance Policies
Developing and implementing comprehensive data governance policies requires a structured approach. These policies should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in business needs and regulatory requirements.
- Policy Development: Establish clear policies covering data definitions, data quality standards, data access controls, and data retention guidelines. These policies should be documented and readily available to all stakeholders.
- Policy Communication: Communicate the policies effectively to all stakeholders through training programs, workshops, and regular updates. This ensures everyone understands their responsibilities and how to comply with the policies.
- Policy Enforcement: Implement mechanisms to monitor adherence to data governance policies. This may include regular audits, data quality checks, and performance reviews.
- Policy Review and Updates: Regularly review and update the policies to reflect changes in business needs, regulatory requirements, and technological advancements. This ensures the policies remain relevant and effective.
Data Retention and Archival Best Practices
Implementing a robust data retention and archival strategy is essential for compliance and efficient data management. This involves defining retention periods for different data types and establishing secure archival processes.
For example, employee payroll data might need to be retained for a longer period due to legal and tax requirements, while performance review data may have a shorter retention period. A clear policy outlining these retention periods and archival procedures is crucial. Consider using secure cloud storage or dedicated archival systems for long-term data preservation.
Data Governance Framework for an HRIS System
A well-defined data governance framework provides a structured approach to managing HRIS data. This framework should Artikel roles, responsibilities, processes, and technologies involved in data management.
| Role | Responsibility | Process |
|---|---|---|
| Data Owner (VP of HR) | Defines data policies, ensures data quality and compliance | Oversees data governance committee, approves policy changes |
| Data Steward (HR Manager) | Manages specific datasets, ensures data accuracy | Conducts data quality checks, resolves data discrepancies |
| Data Custodian (IT Manager) | Manages data storage, security, and access | Implements security measures, manages data backups |
| HR Business Partners | Supports data usage for business decisions | Provides data analysis and reporting |
Reporting and Analytics
Unlocking the power of your HRIS data goes beyond simple record-keeping; it’s about transforming raw information into actionable insights that drive strategic decision-making. Effective reporting and analytics are the key to understanding your workforce, optimizing processes, and achieving your HR goals. This section explores how to design impactful HR reports, leverage key performance indicators (KPIs), and utilize data visualization to effectively communicate your findings.Effective HR reports provide more than just numbers; they offer a clear picture of your workforce’s health and performance, revealing trends and opportunities for improvement.
By strategically selecting the right metrics and presenting them visually, you can easily identify areas needing attention and make data-driven decisions that positively impact your organization. This section delves into the specifics of creating such reports.
Designing Effective HR Reports
Designing effective HR reports requires careful planning and consideration of the intended audience and purpose. Reports should be concise, easy to understand, and focus on key metrics that directly relate to business objectives. Avoid overwhelming the reader with unnecessary data; instead, highlight the most crucial information. Consider using a consistent format and style across all reports for improved readability and ease of comparison.
A well-designed report should answer specific questions and provide clear recommendations for action. For example, a report on employee turnover might highlight departments with high attrition rates, allowing HR to investigate underlying causes and implement targeted retention strategies.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in HR
Several key performance indicators can be tracked using HRIS data to gain a comprehensive understanding of your workforce. These KPIs provide a quantifiable measure of HR effectiveness and allow for continuous improvement. Examples include:
- Employee Turnover Rate: Measures the percentage of employees leaving the company within a specific period. A high turnover rate can indicate issues with employee satisfaction, compensation, or management.
- Time-to-Hire: Tracks the time it takes to fill open positions. A shorter time-to-hire indicates efficiency in the recruitment process.
- Employee Satisfaction: Assessed through surveys and feedback mechanisms, this KPI reveals employee morale and engagement levels.
- Training and Development Costs per Employee: Measures the investment in employee training and development, indicating a commitment to employee growth.
- Cost per Hire: Calculates the total cost associated with recruiting and hiring a new employee.
By monitoring these KPIs, HR professionals can identify trends, areas for improvement, and the overall effectiveness of HR initiatives.
Data Visualization Techniques
Data visualization is crucial for effectively communicating HR insights. Visual representations of data, such as charts and graphs, make complex information easier to understand and interpret. Using appropriate visualization techniques, such as bar charts to compare performance across different departments, line charts to track trends over time, or pie charts to show the proportion of employees in different categories, significantly enhances the impact of your reports.
Interactive dashboards can provide even more dynamic insights, allowing users to explore data in different ways and drill down into specific details. For example, a geographical map could show employee distribution across different regions, highlighting potential recruitment opportunities or areas needing attention.
Sample HR Metrics Report
The following table presents a sample report showcasing key HR metrics for the past quarter. This demonstrates how data can be presented in a clear and concise manner.
| Metric | Q1 2024 | Q2 2024 | Q3 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employee Turnover Rate | 5% | 4% | 3% |
| Time-to-Hire (Days) | 35 | 30 | 28 |
| Employee Satisfaction Score (out of 10) | 7.8 | 8.1 | 8.5 |
| Training Cost per Employee ($) | 500 | 550 | 600 |
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery

In the world of HRIS, where employee data is the lifeblood of an organization, robust data backup and disaster recovery (DR) planning isn’t just a good idea—it’s a necessity. A well-defined strategy safeguards your valuable information from potential threats, ensuring business continuity and minimizing disruption in case of unforeseen events. Without a solid plan, a system failure or security breach could lead to significant financial losses, legal repercussions, and irreparable damage to employee trust.Data loss can stem from various sources, including hardware failures, natural disasters, cyberattacks, human error, or even software glitches.
The consequences can range from minor inconveniences to complete operational paralysis. Therefore, implementing a comprehensive data backup and disaster recovery strategy is paramount for any organization relying on an HRIS system.
Backup Strategies
Choosing the right backup strategy depends on several factors, including budget, the size of your data, recovery time objectives (RTO), and recovery point objectives (RPO). These objectives define how quickly you need to restore your system and how much data loss you can tolerate. Different approaches offer varying levels of protection and cost-effectiveness.
- Full Backups: A full backup copies all data from the HRIS system. It’s time-consuming but provides a complete restore point. Pros: Complete data restoration. Cons: Slow backup process, significant storage space required.
- Incremental Backups: Only changes made since the last full or incremental backup are copied. Pros: Faster backup process, less storage space required. Cons: Longer restore time as multiple backups need to be combined.
- Differential Backups: Copies all changes made since the last full backup. Pros: Faster restore than incremental backups. Cons: Requires more storage space than incremental backups.
- Mirror Backups: Creates a real-time, exact copy of the HRIS database on a separate system. Pros: Near-instantaneous recovery. Cons: High cost, requires significant storage space and resources.
Disaster Recovery Procedures
A comprehensive disaster recovery plan Artikels the steps to take in the event of a major disruption. This plan should detail how to restore HRIS functionality, including data recovery, system restoration, and business continuity measures. Consider these elements:
- Offsite Backup Storage: Storing backups in a geographically separate location protects against local disasters like fires or floods. This could involve cloud storage, a secondary data center, or a secure offsite facility.
- System Recovery Procedures: Detailed, step-by-step instructions for restoring the HRIS system from backups, including network configuration, software installation, and data restoration.
- Communication Plan: A strategy for communicating with employees, management, and other stakeholders during and after a disaster. This includes notification protocols and information dissemination channels.
- Alternative Work Arrangements: Plans for maintaining HR functions during downtime, such as using alternative systems or remote work arrangements.
Testing Backup and Recovery Processes
Regular testing is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of your backup and disaster recovery plan. This involves simulating different disaster scenarios and verifying that the system can be restored within acceptable RTO and RPO limits.
- Restore Tests: Periodically restore the HRIS system from backups to verify data integrity and the functionality of the recovery process. This should be done using different backup types and restoration methods.
- Failover Tests: Simulate a system failure by switching to a secondary system or a cloud-based backup to assess the speed and efficiency of the failover process.
- Tabletop Exercises: Conduct regular tabletop exercises to review the disaster recovery plan and identify potential weaknesses or areas for improvement. This involves simulating various scenarios and discussing the appropriate response strategies.
Data Migration and System Upgrades
Upgrading your HRIS or migrating to a new system is a significant undertaking, demanding meticulous planning and execution. A successful transition ensures minimal disruption to HR operations and maintains the integrity of your valuable employee data. Failing to properly plan can lead to costly downtime, data loss, and significant frustration for both HR staff and employees.Data migration and system upgrades are complex processes that require careful consideration of various factors.
A well-defined strategy, encompassing data cleansing, testing, and validation, is crucial for a smooth transition. This section will delve into best practices to ensure a successful migration and upgrade.
Data Migration Strategies
Minimizing data loss during migration requires a multi-pronged approach. A thorough assessment of the existing HRIS data is the first step, identifying any inconsistencies, duplicates, or outdated information. This cleansing process should involve data validation checks and standardization to ensure data quality. Next, a robust migration plan should be developed, outlining the specific steps, timelines, and responsibilities for each phase of the process.
This plan should include a detailed data mapping process to ensure accurate transfer of data between systems. Finally, a phased rollout, starting with a pilot group, allows for early identification and resolution of any unforeseen issues. This iterative approach significantly reduces the risk of widespread problems during the full migration.
Data Validation After Migration
Post-migration data validation is essential to verify the accuracy and completeness of the transferred data. This involves comparing the data in the new system against the original data source to identify any discrepancies. Data validation techniques can include automated checks, manual reviews, and reconciliation processes. Any inconsistencies should be thoroughly investigated and rectified. Regular reporting and monitoring post-migration are also crucial to identify any emerging issues and ensure the ongoing integrity of the data.
Challenges and Mitigation Strategies During HRIS System Upgrades
HRIS system upgrades often present unforeseen challenges. For example, incompatibility between the old and new systems can lead to data loss or corruption during the transfer process. Another common challenge is the lack of adequate training for HR staff on the new system, leading to inefficiencies and errors. Furthermore, insufficient testing before the go-live date can result in system failures and data inaccuracies.
To mitigate these challenges, thorough testing and validation should be conducted throughout the upgrade process. Comprehensive training programs for HR staff are also crucial to ensure smooth system adoption. Finally, establishing a robust communication plan to keep stakeholders informed of the progress and any potential disruptions minimizes disruptions and ensures buy-in from all involved. For instance, a large multinational corporation might pilot the upgrade in a smaller office before a full-scale rollout, using the experience to refine the process and identify potential issues before impacting the entire organization.
User Training and Support

A robust HRIS system is only as good as the people who use it. Effective HRIS data management relies heavily on well-trained staff who understand the system’s capabilities and limitations. Investing in comprehensive user training and ongoing support is crucial for maximizing the system’s value and minimizing errors. This section Artikels best practices for designing training programs, providing ongoing support, and leveraging user feedback to continuously improve HRIS data management processes.Effective user training is paramount for successful HRIS implementation and ongoing data integrity.
Without proper training, staff may misuse the system, leading to inaccurate data, compliance issues, and ultimately, hindering the HR department’s efficiency. A multi-faceted approach, combining various learning styles, ensures broader comprehension and retention.
Designing a Training Program for HR Staff
A well-structured training program should encompass various learning methods, catering to diverse learning styles. The program should begin with an overview of the HRIS system, its functionalities, and its importance in the organization. This should be followed by hands-on training sessions where staff can practice data entry, data validation, and report generation. The curriculum should cover data security protocols, compliance requirements, and best practices for data management.
Consider incorporating interactive elements such as quizzes, simulations, and group exercises to enhance engagement and knowledge retention. Regular refresher courses and advanced training modules should also be offered to keep staff updated on system changes and best practices. Finally, a post-training assessment can gauge understanding and identify areas requiring further attention.
Providing Ongoing User Support and Documentation
Ongoing support is as crucial as initial training. A dedicated help desk or support team should be available to answer questions, troubleshoot issues, and provide guidance. Comprehensive documentation, including user manuals, FAQs, and video tutorials, should be readily accessible to all users. Regular updates to the documentation are vital to reflect any system changes or improvements. Consider creating a knowledge base or online forum where users can share information and support each other.
Proactive communication, such as regular newsletters or announcements, can keep users informed about new features, updates, and best practices.
The Importance of User Feedback in Improving HRIS Data Management Processes
User feedback is invaluable for continuous improvement. Regular surveys, feedback forms, and focus groups can help identify areas where the system or training could be improved. Analyzing user feedback can reveal common errors, usability issues, and areas of confusion. This information can be used to revise training materials, update documentation, and improve the system’s design. Creating a culture of open communication and feedback ensures that the HRIS system remains relevant, user-friendly, and effective.
Acting upon user feedback demonstrates a commitment to continuous improvement and enhances user satisfaction.
Resources for HR Staff Regarding HRIS Data Management
Providing readily accessible resources empowers HR staff to manage data effectively. This includes:
- User manuals and FAQs: Comprehensive guides detailing system functionalities and troubleshooting common issues.
- Video tutorials: Step-by-step guides demonstrating key tasks and processes.
- Online knowledge base: A centralized repository of information, FAQs, and solutions to common problems.
- Internal support team contact information: Easy access to dedicated support staff for assistance.
- Compliance guidelines and policies: Clear documentation of relevant data privacy and security regulations.
- Best practices guides: Documents outlining recommended procedures for data entry, validation, and reporting.